Difference between revisions of "ThreadScope Tour"
(→Basic skills: remove extraneous p tags from li) |
(maybe better wording?) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ |
__NOTOC__ |
||
| − | |||
''A guided tour of ThreadScope'' |
''A guided tour of ThreadScope'' |
||
| + | Have parallel Haskell but not enough performance? Try [[ThreadScope]]! It won't fix your program for you, but it may help you to understand what is slowing your program down. We in the ThreadScope team have put together this user guide to help you get started and make the most of this tool. |
||
| − | In this tutorial, we'll be working through concrete examples on using ThreadScope to debug the performance of parallel programs. |
||
| − | We aim to keep each module in |
+ | You can also treat this manual as a tutorial. We'll be working through concrete examples on using ThreadScope to debug the performance of parallel programs. We aim to keep each module in this tutorial self-contained, so you can either follow the progression suggested or jump to just the sections we need. |
| + | <div class="subtitle">Software</div> |
||
| − | Note that you will need: |
||
| + | This tutorial is written with the following software versions in mind. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | == Getting Started == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="subtitle">Getting started</div> |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ThreadScope-ch8.png|thumb]] |
||
# [[ThreadScope_Tour/Install|Installation]]: install ThreadScope and run a sample trace |
# [[ThreadScope_Tour/Install|Installation]]: install ThreadScope and run a sample trace |
||
| − | # [[ThreadScope_Tour/Run|Hello world]]: |
+ | # [[ThreadScope_Tour/Run|Hello world]]: run ThreadScope on a small test program |
| − | = |
+ | <div class="subtitle">Basic skills</div> |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ThreadScope-sudoku2.png|thumb]] |
||
<ol start="3" style="list-style-type: decimal;"> |
<ol start="3" style="list-style-type: decimal;"> |
||
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Statistics|Initial statistics]]: collect some simple statistics</li> |
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Statistics|Initial statistics]]: collect some simple statistics</li> |
||
| − | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Profile|Profile]]: examine the profile for a real program</li> |
+ | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Profile|Profile]]: examine the profile for a real program </li> |
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Profile2|Profile 2]]: examine the profile for an improved program</li> |
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Profile2|Profile 2]]: examine the profile for an improved program</li> |
||
| − | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Zoom|Zoom]]: |
+ | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Zoom|Zoom]]: zoom in to see performance behaviour at a finer resolution</li> |
| + | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Bookmark|Bookmark]]: place a temporary marker in the eventlog</li> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | = |
+ | <div class="subtitle">Digging into a program with spark events</div> |
| + | [[Image:spark-lifecycle.png|thumb]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<ul> |
<ul> |
||
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/RTS|GHC RTS flags]]: a subset of flags relevant to ThreadScope</li> |
<li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/RTS|GHC RTS flags]]: a subset of flags relevant to ThreadScope</li> |
||
| − | <li>[[: |
+ | <li>[[Special:FilePath/spark-lifecycle.png|Spark lifecycle]]: Lifecycle of a spark</li></ul> |
| + | </li> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
</li> |
</li> |
||
| − | <li |
+ | <li>[[ThreadScope_Tour/Spark2|Spark rates 2]]: spark debugging continued</li> |
| ⚫ | |||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
| − | = |
+ | <div class="subtitle">Reference</div> |
* [[ThreadScope_Tour/Downloads|Downloads]]: examples used in this tutorial |
* [[ThreadScope_Tour/Downloads|Downloads]]: examples used in this tutorial |
||
| + | ''This tutorial was initially written by Well-Typed in the context of the [[Parallel GHC Project]]. [mailto:eric@well-typed.com Feedback] would be most appreciated!'' |
||
| − | == Planned == |
||
| + | [[Category:ThreadScope]] |
||
| − | # [[ThreadScope_Tour/Trace|Trace]]: custom events |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 07:47, 17 May 2012
A guided tour of ThreadScope
Have parallel Haskell but not enough performance? Try ThreadScope! It won't fix your program for you, but it may help you to understand what is slowing your program down. We in the ThreadScope team have put together this user guide to help you get started and make the most of this tool.
You can also treat this manual as a tutorial. We'll be working through concrete examples on using ThreadScope to debug the performance of parallel programs. We aim to keep each module in this tutorial self-contained, so you can either follow the progression suggested or jump to just the sections we need.
This tutorial is written with the following software versions in mind.
- ThreadScope 0.2.1
- GHC 7.4. (earlier versions work, but lack more advanced features like spark events)
- Installation: install ThreadScope and run a sample trace
- Hello world: run ThreadScope on a small test program
- Initial statistics: collect some simple statistics
- Profile: examine the profile for a real program
- Profile 2: examine the profile for an improved program
- Zoom: zoom in to see performance behaviour at a finer resolution
- Bookmark: place a temporary marker in the eventlog
- Consolidate: tease out the sequential parts of code
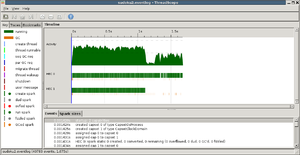
- Spark overview
- GHC RTS flags: a subset of flags relevant to ThreadScope
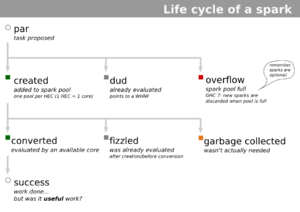
- Spark lifecycle: Lifecycle of a spark
- Spark rates: study spark creation/conversion
- Spark rates 2: spark debugging continued
- Downloads: examples used in this tutorial
This tutorial was initially written by Well-Typed in the context of the Parallel GHC Project. Feedback would be most appreciated!